Basics of 2D Coordinate Geometry
Basics of 2D Coordinate Geometry: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Coordinate Geometry, 2D Coordinate System, Rectangular Cartesian Coordinate System, Quadrants of 2D Plane, A Point in 2D Coordinate System, Distance of a Point from the Axes, Distance between Two Points, etc.
Important Questions on Basics of 2D Coordinate Geometry
In what ratio does the point divides the line segment joining the points and ?
The distance between points and is
From the point on the circle , a chord is drawn and extended to a point such that . The equation of the locus of is
If the area of a triangle is sq. units with vertices at and , then the value of is
If and are both in G.P. with the same common ratio, then the points and
Consider a rigid square as in the figure with and on the and -axes, respectively.
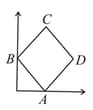
When and slide along their respective axes, the locus of forms a part of
What is the distance of point from the origin?
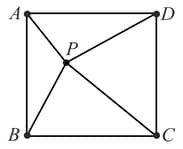
Square has side length Point lies inside the square so that and The centroids of and are the vertices of a convex quadrilateral. The area (in sq. units) of the quadrilateral is
Define coordinate system. Find the quadrant belongs to.
Define coordinate system. Find the quadrant belongs to.
Define coordinate system. Find the quadrant belongs to.
Define coordinate system. Find the quadrant belongs to.
Define coordinate system. Find the quadrant belongs to.
If a square where undergoes the following transformations successively,
Then the final figure would be a _______.
Given points and as the origin, find the locus of a point such that area of triangle is times the area of triangle
For two points and is a point such that then locus of is
If the equation of a line which divides the line segment joining the points and in the ratio and is also perpendicular to it, is , then the value of is equal to
Let be any two points on a circle of radius centred at the origin such that If is the point of intersection of the tangents to the circle at and then the locus of the point is
If the point divides the line segment joining the points and , externally in the ratio , then the locus of is
Let be the focus of parabola and be any point on it. If divides the line segment in the ratio then the locus of is
